1st Hour - History of Astronomy Quiz
After test please complete the virtual laboratory.
2nd Hour - History of Astronomy Quiz
After test please complete the virtual laboratory.
5th Hour - History of Astronomy Quiz
After test please complete the virtual laboratory.
History of Astronomy Notes:Astronomy is the science that studies the universe. It includes the observation and interpretation of celestial bodies and phenomena.
Civilization Contributions
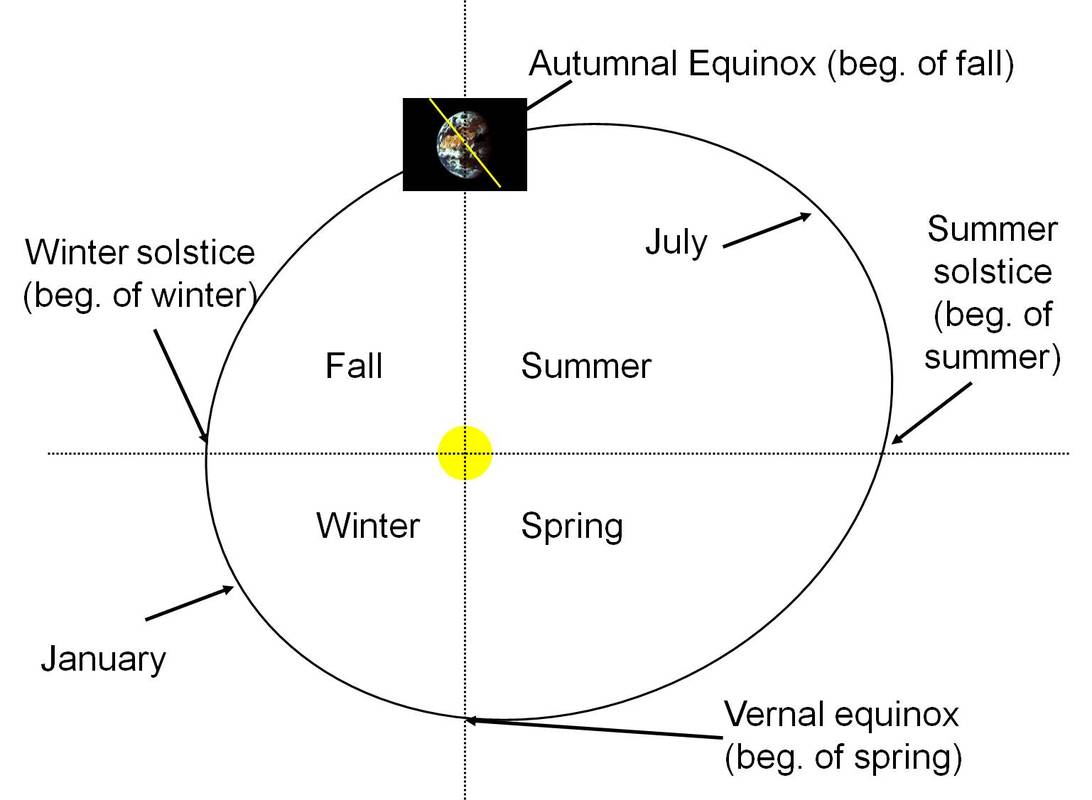
Geocentric Model = Ptolemy (Greek Astronomer) In the ancient Greeks’ geocentric model, the moon, sun, and the known planets—Mercury, Venus, Mars, and Jupiter--orbit Earth. Heliocentric Model = Nicolaus Copernicus In the heliocentric model, Earth and the other planets orbit the sun. Copernicus concluded that Earth is a planet. He proposed a model of the solar system with the sun at the center. Tycho Brahe designed and built instruments to measure the locations of the heavenly bodies. Are all four seasons equally long?
|
Kepler discovered three laws of planetary motion:
1. Orbits of the planets are elliptical. 2. Planets revolve around the sun at varying speed. 3. There is a proportional relationship between a planet’s orbital period and its distance to the sun. Galileo Galilei (1564—1642) used a new invention, the telescope, to observe the Sun, Moon, and planets in more detail than ever before. Galileo’s most important contributions were his descriptions of the behavior of moving objects and the telescope. English scientist - Sir Isaac Newton (1642—1727) explained gravity as the force that holds planets in orbit around the Sun. Although others had theorized the existence of gravitational force, Newton was the first to formulate and test the law of universal gravitation. The universal law of gravitation, helped explain the motions of planets in the solar system and how our Sun is pulled towards the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. Most scientists believe the Big Bang Theory which discussed the creation of the universe. |